EXPLORING THE ROOTS OF EVOLUTIONARY THEORY
Awareness of biological evolution emerged over centuries through the cumulative observations of many naturalists, biogeographers, comparative anatomists, and paleontologists. When Darwin and Wallace in the mid-1800s arrived at the idea of evolution by natural selection, they had been influenced not only by their own travels and observations, but also by the writings of many of their predecessors. Darwin’s ideas were also influenced by his travels as a young naturalist on the H.M.S. Beagle. The islands he explored off the coast of Ecuador, the Galapagos, are hotbeds of evolutionary change. However, as you will see, Darwin did not entirely recognize the importance of these islands until after he returned from his voyage.
Activity
In this activity you will access the evolution section of the University of California’s Museum of Paleontology to explore some of the roots of evolutionary biology. You will then visit the Why Files site to learn about Darwin’s voyage to the Galapagos and the current state of these islands.
Part 1.
Use your browser to go to the “History of Evolutionary Thought” exhibit at the University of California Berkeley
Museum of Paleontology at http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/evothought.htmlUse the links in this section to learn about and briefly describe the background and scientific contribution of each of the following people:
1. Erasmus Darwin-Charles Darwin’s grandfather, Erasmus Darwin, was one of the leading intellectuals of eighteenth century England. Erasmus Darwin was a respected physician, a well known poet, philosopher, botanist, and naturalist.
- formulated one of the first formal theories on evolution in Zoonomia, or, The Laws of Organic Life
- discuss ideas of how life originated from a single common ancestor
2. Jean Baptiste Lamarck-Lamarck was the first man whose conclusions on the subject excited much attention. This justly celebrated naturalist first published his views in 1801. . . he first did the eminent service of arousing attention to the probability of all changes in the organic, as well as in the inorganic world, being the result of law, and not of miraculous interposition.
3. Georges Cuvier
Without a doubt, Georges Cuvier possessed one of the finest minds in history. Almost single-handedly, he founded vertebrate paleontology as a scientific discipline and created the comparative method of organismal biology, an incredibly powerful tool. It was Cuvier who firmly established the fact of the extinction of past lifeforms. He contributed to alot of research in vertebrate and invertebrate zoology and paleontology, and also wrote and spoke on the history of science.
4. Thomas Malthus
Malthus was a political economist who was concerned about, what he saw as, the decline of living conditions in nineteenth century England. He blamed this decline on three elements: The overproduction of young; the inability of resources to keep up with the rising human population; and the irresponsibility of the lower classes. To combat this, Malthus suggested the family size of the lower class ought to be regulated such that poor families do not produce more children than they can support. Does this sound familiar? China has implemented a policy of one child per family (though this applies to all families, not just those of the lower class).
Part 2.
Use your browser to go to the Why Files’ “Treasures of Evolution Island” at http://whyfiles.org/125galapagos/index.html
Use the information from Sections 3 and 4 to answer the following questions:
1. What interesting evidence of geological change did Darwin observe while visiting the Galapagos?
The Galapagos Islands are volcanic which means that the animals that lived there must have come from somewhere else, but those animals lived no where else in the world. This meant that their ancestors must have come from somewhere else, and evolved into the creatures Darwin saw on the island currently. Because the creatures on The Galapagos where different then those in other places but very similar
2. What did Darwin learn about the Galapagos finches when he returned to England? What vital information had he neglected to record when he collected them?
3. Describe the distribution pattern of Galapagos mockingbirds. What question did this raise in Darwin’s mind?


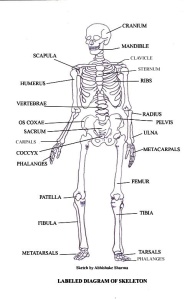
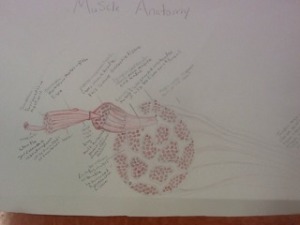


 this is the cardiac muscle ,skeletal muscle involuntary muscle teased .
this is the cardiac muscle ,skeletal muscle involuntary muscle teased . 
